Global Positioning System commonly in trend as GPS is a type of satellite navigation system designed to provide the position and timing information of the user. Here the name itself is indicating that GPS includes a set of elements that forms a system that helps in globally locating the presence of users at a specific point on the earth.
It is a US-owned technology that provides location and timing information of the users over land, sea, or air by the use of satellites.
In simplest terms, GPS can be defined as a system that is a collection of navigation satellites broadcasting signals to the GPS receiver (for example, the one within your mobile phone). On getting the signal, the distance is calculated and one can find out his/her presence at the location where the device is present.
Content: Global Positioning System
History of Global Positioning System
Before GPS came into existence, navigators were trying to develop such a system that can help them in locating their position at any point over the globe with accuracy so that they can reach their desired destination without any difficulty. After a year of efforts, a solution for the same came in the 1970s. The US – Department of Defence in the year 1978 launched a Navigation System with Timing and Ranging (named as NAVSTAR) for accurate positioning of objects using satellites on or near the earth surface.
In the year 1993, the navigation system was developed successfully under the operation of the US Air Force that had used 24 satellites and was named GPS i.e., Global Positioning System.
The US government owns GPS that is a multipurpose space-based navigation system controlled by the United States Air Force and serves defense, civil, commercial, scientific, and security-related fields.
GPS Principle
In our previous content, on navigation satellites, we have discussed that GPS is a type of satellite navigation system designed with the aim to provide services like position, time, and velocity to the users by the use of satellites. GPS has brought great advancement in satellite-based navigation systems.
The principle of operation of GPS is Trilateration. Basically, it makes use of 4 satellites of known orbital positions that transmit codes towards the user. To have the accurate position of the user on or near the earth’s surface, codes from three satellites are considered while the fourth one is used to make the necessary changes related to timing error. The GPS device must interpret the signal coming from the satellites in space to have its exact location. Let us understand how GPS operates in detail:
How does a GPS work?
We have already discussed in the beginning that, nowadays, GPS has gained worldwide popularity and thus is present in vehicles (like cars), within smartphones, in watches, shipping containers, missiles, etc. It helps in tracing location as well as getting the distance that is required to be traveled.
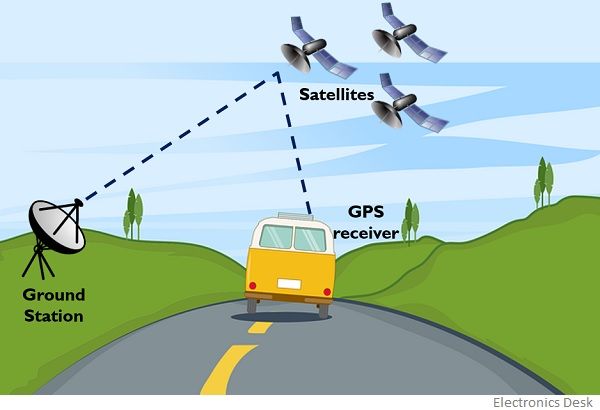
For the operation of the GPS navigation system, various segments work together in order to generate information regarding location and time. These segments are explained below in brief:
- Space segment: This includes the satellites present in space and is regarded as one of the major components that build the navigation system. The satellites in space transmit signals to the users to their respective geographical position with respect to time. These satellites orbit at around 20000 km above the earth’s surface with a speed nearly of 14000 km/hr.
A GPS uses 24 satellites situated in 6 different earth-centered orbits thus each having 4 satellites. - Ground Control segment: This segment is quite crucial functionality-wise and it consists of the master control station along with monitoring stations and the ground-based antenna. This unit monitors transmission and helps in tracking the satellite moving in space. The tracking of satellites is not easy because satellites move in inclined orbits thus to get tracking-related information around 107 satellites are available over the globe.
- User equipment segment: The user equipment segment is nothing other than the GPS receiver and transmitter like various telematics devices i.e., watches, smartphones, etc.
We have mentioned in the previous section that GPS works on the principle of trilateration. Now, let us proceed to understand how GPS utilizes the principle of trilateration to provide the exact location of the user.
Each satellite orbiting earth in space broadcasts a microwave signal towards the earth. This navigation signal is nothing other than the message containing information regarding acquisition and position calculation. This microwave signal is picked by the GPS receiver and using the information content, the device determines the distance between satellite and device.
Generally, the incoming signal from the satellite is a pseudorandom code showcasing the information regarding the specific satellite which is sending the signal along with ephemeris data that includes the data relative to the orbital position of the signal sending satellite and transmitting time.
The use of multiple satellites helps to get accurate location information. A satellite does not provide angular information thus the determination is done by keeping in mind that the location can be present anywhere on the spherical region of the earth. So, initially, three out of four satellites in space broadcast signals. Each broadcasting satellite makes its respective circles in such a way that the distance between the satellite and the GPS device acts as the radius of that particular circle.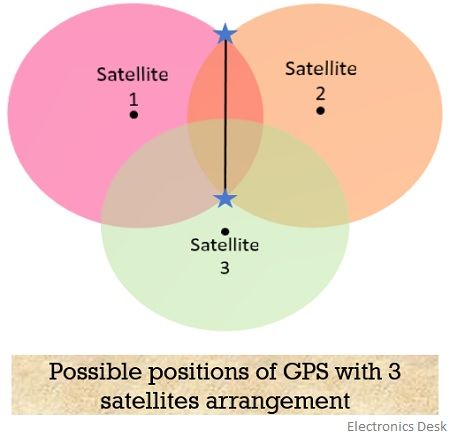
As we know that the orientation is three-dimensional thus, the resultant will be a sphere rather than a circle. Hence, there will be two-point interaction so, the point which is closer to the surface of the earth is selected. Further, when the device moves, then with the change in its orbital position, the radius also varies this gives rise to the new sphere, and hence resultantly a new point is located by the device on or near the earth’s surface.
Factors Affecting GPS accuracy
The accuracy of the result obtained by GPS navigation shows dependency on the following factors:
- The atmospheric effects, including ionospheric delays, storms, etc.
- Some physical obstructions due to bodies of large masses such as mountains, buildings, trees, etc.
- Numerical miscalculations are associated with the hardware of devices that are not up to the desired specifications.
- Sometimes artificial interference also acts as a hurdle in getting the desired location and generally, jammers offer artificial intelligence.
Applications of GPS
The various applications of GPS include the determination of accurate position, monitoring movement, time-related measurements, location detection, etc. Thus, these are widely used in aircraft, ships, farming equipment, mapping, telecommunication, transportation, scientific activities like weather forecasting, environmental protection.