The crucial difference between conductor, semiconductor and insulator rely on their level of conductivity. Conductors are basically the materials that allow easy flow of electric current, hence exhibiting high conductivity, semiconductors are the materials that possess moderate conductivity. As against, insulators are the materials that prevent the flow of charge through them, thus exhibiting low conductivity.
This is the major factor that distinguishes the three. However, some other differences exist between conductor, semiconductor and insulator which we will discuss later. But, before moving to that look at the contents that are to be discussed under this article.
Content: Conductor Vs Semiconductor Vs Insulator
Comparison Chart
| Parameter | Conductor | Semiconductor | Insulator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Forbidden energy gap | Not exist | Small (1 eV) | Large (>5 eV) |
| Conductivity | High (10-7 mho/m) | Medium (10-7 to 10-13 mho/m) | Very Low (10-3 mho/m) Almost negligible. |
| Resistivity | Low | Moderate | High |
| Flow of current | Due to movement of free electrons. | Due to movement of electrons and holes. | Almost negligible but only due to free electrons. |
| Temperature coefficient of resistance | Positive | Negative | Negative |
| Charge carriers in conduction band | Completely filled | Partially filled | Completely vacant |
| Charge carriers in valence band | Almost vacant | Partially filled | Completely filled |
| Example | Copper, Aluminium, graphite etc. | Silicon, Germanium, arsenic etc. | Paper, rubber, glass, plastic etc. |
| Applications | Conducting wires, Transformers, in electrical cords etc. | Diodes, transistors, optocouplers etc. | Sports equipment, home appliances etc. |
Definition of Conductor
Conductors are the substances that permit easy flow of electric energy through them. More specifically, we can say, it permits easy flow of electron from an atom to the other when a proper electric field is applied to it. These are the material, that possesses the highest conductivity among the three.
Now, the question that strikes our mind is what is conductivity?
So, it the property of a material by which it allows a large amount of current to flow through it. Majorly the movement of electrons inside the material is responsible for its conduction. And these electrons show movement when a certain voltage is applied to it. This voltage applies a force to the electrons due to which it easily starts moving from valence band to conduction band.
Thus, these are good conductors of electricity.
Let us have a look at the energy level diagram of conductors:
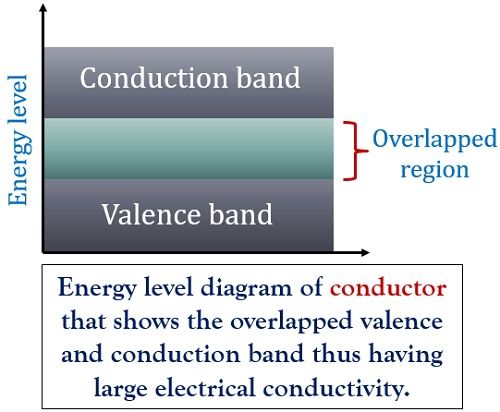
As the two bands i.e., valence band and conduction band are overlapped with each other. Thus when some certain voltage is applied to such materials, then electrons easily moves from valence band to conduction band due to the influence of the electric field. This movement of charge carriers generates a large electric current through the device.
Definition of Semiconductor
Semiconductors are the materials that possess the property of electrical conductivity less than conductors. The charge carriers in case of semiconductors are electrons and holes.
When the temperature is absolute zero, then no any movement of charge carriers takes place in case of semiconductors. In such case, it behaves as insulators. But in order to have a considerable flow of charge carriers to take place certain potential must be provided to them that can excite the electrons to another energy level. Thereby, generating electric current.
Let us have a look at the energy level diagram of semiconductors:
![]()
As we can see in the figure above that, the energy band gap between the valence band and conduction band is present. Though this energy difference was not present in the previously discussed case of conductors.
In the case of semiconductors, the two bands do not overlap thus a small energy difference exists between them. So, the electrons in the valence band cannot automatically excite in order to move to the conduction band. But, on applying certain voltage, the electrons in the valence band gains sufficient energy and jumps to the conduction band.
Definition of Insulator
Insulators are the materials that are not good conductors of electric charges. As in the case of insulators, current cannot flow easily through them. The energy band gap is so high in case of insulators that even applied potential does not excite the electrons from valence band to conduction band. But as these possess negative temperature coefficient of resistance hence with the increase in temperature the resistance offered by it decreases.
Let us have a look at the energy level diagram of an insulator:
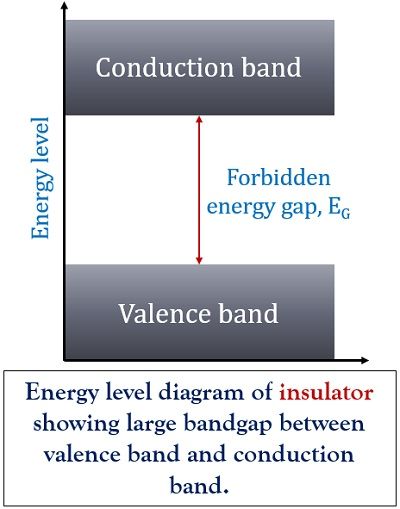
Here, as we can see that large band gap exists between valence and conduction band. This large band gap does not allow the electrons to jump into the conduction band. Hence, the current flow is not possible. The band gap in case of the insulator is larger as compared to both conductors and insulators.
However, there exists a breakdown case of insulating materials in which, when an extremely high temperature is provided or supplied then it causes the electrons to overcome the large energy difference thereby moving to the conduction band.
Key Differences Between Conductor, Semiconductor and Insulator
- The factor that generates a key difference between conductor, semiconductor and insulator is that the energy gap between the conduction band and valence band does not exist as the two bands overlap in case of the conductor.
On the contrary, the energy gap between valence and conduction band is small in case of semiconductors. While large energy difference exists between the two bands in case of insulators. - As conductors allow a large flow of electric current thus exhibits low resistivity as compared to semiconductor whose resistivity is moderate. On the other side, insulator possesses the highest resistivity among all.
- Conductors are highly conductive in nature while semiconductors possess moderate conductivity. As against, the conductivity of insulators is almost negligible.
- Conductors are the materials that exhibit a positive temperature coefficient of resistance, as resistance increases with the increase in temperature. While semiconductors and insulators possess negative temperature coefficient of resistance as their resistivity decreases with the increase in temperature.
- In the case of conductors, the conduction band is completely filled, in semiconductor, it is partially filled while in insulators conduction band is totally vacant.
- The valence band in conductors is almost vacant, in semiconductors, it is partially filled as some electrons are present in the conduction band due to small band gap. However, the valence band is completely filled in case of insulators because there exists a large band gap between valence and conduction band.
- The common conductors are copper, aluminium, graphite, iron etc. Silicon and germanium are examples of semiconductors. While common insulators are paper, rubber, glass, plastic etc.
Conclusion
So, from the above discussion, we can conclude that the movement of electrons from valence band to conduction band is responsible for the flow of current. The presence of electrons at the conduction band decides the conducting level of the material. Therefore, the conductivity level of semiconductors somewhere lies between conductors and insulators.
The definitions of conductor, semiconductor and insulator which given by you that’s good, easy to understand and also good for teaching material. Thank you…. 🙂
perfect……thank you….words seem less to describe my happiness to know the topic nicely….and also with this, I was able to complete my assignment in a proper way…thanks a lot