Demand Assigned Multiple Access is a technique used for the purpose of assigning communication channels to the end-users in response to the requests received from the respective user terminals. It is abbreviated as DAMA and is a crucial technique that supports satellite communication and mainly finds uses in systems that consist of VSATs.
The word ‘demand’ in ‘demand assigned multiple access’ is itself indicating that here the resources are accessed by multiple users as per their demand. This shows that there is no pre assigning of resources/channels in DAMA. Thus, regarded as a channel allocation technique to users and mainly used for the purpose of handling voice and data traffic.
Content: Demand Assigned Multiple Access
Introduction
Before exploring the DAMA, we must know what multiple access actually means?
We all know that in order to maintain communication between two ends we need to have proper resources like the two terminal stations that are ready for communication must have a channel between them. In a distributed network having multiple numbers of subscribers, it becomes quite difficult to allot a specific channel permanently to the two end-users as this will result in a quite bulky network orientation. So, to overcome this major disadvantage of multiple user networks, multiple access schemes are used.
Multiple access scheme in communication allows efficient sharing of the common channel by many users distributed over a geographical location for the purpose of communicating from one end to another. However, when multiple users share a common channel then there must be some criteria over which their access over the channel must be defined. These criteria can be frequency, time, or code.
But, a sub-classification also exists where the channels under frequency, time, or code are either permanently or on-demand assigned to the various users. This gives rise to fixed assigned multiple access (FAMA) and demand assigned multiple access techniques.
Need for DAMA
DAMA was introduced as a method to overcome the downside of FAMA. Let us understand this-
Basically, FAMA is a scheme where the resources/channels are assigned by initial planning on a fixed basis. This means that the channels are assigned permanently to the users and when not used the specific time or frequency slot gets wasted as it cannot be assigned to any other user. The permanent allocation of the channel without the consideration of its usage makes the technique quite inefficient.
Thus, to deal with the inefficiency of the FAMA, the demand assigned multiple access technique is used by various multiple access systems. The DAMA allows the resource/channel allocation to the users on the basis of requirement. Thus, there is no fixed allotment and the channel can be utilized by the users according to their need.
What is Demand Assigned Multiple Access?
DAMA is a technique whose principle of operation is an ‘as-required basis’ and does not depends on any fixed pre-planning. Thus, it supports the allotment of channels to the users according to their needs. It offers the flexibility in using resources as and when required as it centrally allocates the network resources.
DAMA supports the use of resources by another channel just after one channel has finished using it. In DAMA, the only thing that matters is checking for the availability of the resource at the time of its requirement. The word channel here corresponds to the pair of the carrier frequency (i.e., one for transmit and the other for receive).
Suppose we are having a DAMA of 7 channels then it will only support 7 simultaneous conversations. However, there can be more than 7 multiple nodes that can use the channels after the set of 7 nodes are done with their operation.
Like if the DAMA is incorporated under different time slots then the various users can use the same channels in different time slots. As against, if the DAMA incorporates FDM then there will separate frequency allotment under the complete common channel for each individual user at the same time. Hence, this will help in reducing the chances of data collision or incorrect transmission.
In the previous article, we have discussed asynchronous transfer mode, which was universally adopted to ensure transmission over a broadband satellite network. DAMA offers combining of satellite channels in a bulk and allows the data transmission and reception between users. But, it depends on the type of network that how it prioritizes the users, generally, it is a first come first serve basis.
Operation of DAMA
There are two fundamental methods by which demand assigned multiple access can be carried out which are as follows:
Polling Method: In this method, a master station sequentially polls all the earth stations connected to it in order to check for the call request. Once the call requests are received by the master station then it allots available slots from the frequency pool to the earth station which has sent the requests. However, with the increase in the number of users, polling delay also increases.
Centrally controlled random access method: In this method, the master station does not regularly poll the earth stations but the earth station requests the master station whenever it needs a slot from the channel. On receiving a request if the slot is available then the master station allots it and once the session gets over then the frequency returns to the pool. However, there is a condition for unavailability of the requested slot and in that case, the master station keeps a blocked call request in the queue.
To understand the process of demand assigned multiple access consider the distributed demand assigned network consisting of common signaling channel (CSC):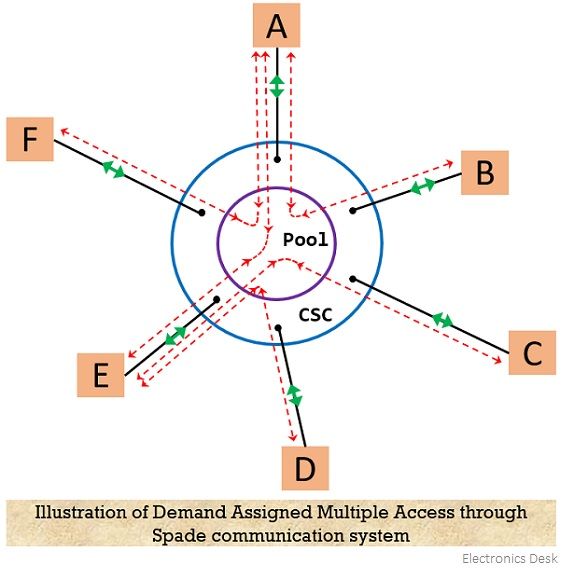
From the above figure, it is clear that 6 earth stations (A, B, C, D, E, F) form a separate connection with the CSC where each station holds a list of frequencies that can be utilized for operation. However, according to the use of the frequency by various stations, this list undergoes timely updations through the common signaling channel. This helps to reduce the chances of the ambiguity of the use of pair of frequencies by different earth stations.
Let us understand how DAMA takes place by considering that a conversation is built between B and E where B starts the call towards station E. So, initially choosing of a pair of frequencies (i.e., uplink, and downlink) by station B is done from the list of available ones and further the information is sent to the station E through the CSC. After getting the signal, if E is ready for circuit completion then that station must send acknowledgment towards B via CSC. After the circuit between stations, B and E is formed then CSC will send a signal to other earth stations for the removal of that particular pair of frequencies from their lists.
Hence, in this way, by selecting a pair of frequencies from the pool, the conversation can be built and once the conversation gets over between the two stations then that pair of frequencies will be available for further use by other stations.
It is to be noted here that the duration of 600 ms is needed for initiating a call and receiving an acknowledgment from the partner station i.e., for circuit completion. However, in the meanwhile, there is a possibility that the chosen frequency is selected by any other pair of stations in the network, and their circuit is built. In such a case, there will be an intimation by the update in available frequency by the CSC, and station B will automatically select another frequency pair from the pool without waiting for acknowledgment from E.
After the completion of the conversation, the circuit will be cut off and the pair of frequencies in use will be given back to the pool. Also, the information regarding the updations of lists at the earth station will get transmitted by the CSC. A unit is present at each earth station named demand assignment signaling and switching and is used to form a connection with the CSC and is responsible for sending and receiving the signals. Such a system is known as the Spade system.
Advantages
- It offers efficient resource utilization by allotting resources after request.
- There are less chances of resource wastage as resources are assigned only till the duration of conversation or data burst.
- It is cost-effective as its payable amount is based on its use.
- It offers a reduction in satellite bandwidth requirements for the operation of the whole network.
Disadvantages
- Increased complexity as a separate unit is required at each earth station for establishing a connection between the stations that contains information regarding the channel in use.
- Sometimes the delay is quite large because of the high load network.
Hence, we can say that the DAMA favors the use of resources according to the need of the subscriber by assigning the transponder channels on the priority of first come, first serve basis, rather than assigning permanently at the initial stage without the confirmation of usage.