A satellite constellation is a collection of similar types of man-made satellites operating as a single unit in space. The satellites in the constellation are synchronized as a unit to orbit the earth in an optimal manner. Thus, we can say, satellite constellation consists of a group of various satellites deployed at the same altitude and inclination.
Satellite constellation forms the base of the field of communication and networking. GPS is regarded as one of the best-known constellations which use 24 satellites for navigation purposes. However, at a time active participation of only 4 satellites takes place.
Content: Satellite Constellation
Need for Satellite Constellation
A single satellite in space offering communication services is designed to cover only a specific part of the world. However, in order to meet proper telecommunication requirements, a number of satellites must be used that can combinedly function as a unit and hence complete coverage can be obtained. To achieve complete coverage not only a single but a number of satellites are used which is regarded as a satellite constellation.
It is to be noted here that the constellation of satellites is generally made using low earth orbit satellites i.e., LEO satellites. Now, the question arises-
Why LEO satellites are used for satellite constellation and not GEO satellites?
The use of LEO satellites in satellite constellation is due to the fact that LEO satellites are designed to offer operation over a smaller region thus these move with high angular velocity to remain in their orbit. Thus, a number of such satellites moving with high angular velocity offer continuous coverage over the complete region. The geostationary satellites are not suitable for such operations as these possess angular velocity similar to the velocity with which the earth is rotating because it has a comparatively larger region to cover than the LEO satellites.
LEO constellation is regarded as a less complex higher altitude system with fewer satellites offering the use of limited available frequencies for communication across the complete earth’s surface at various areas or spot beams. Hence, offers simultaneous transmission to long distances thereby offering great capacities.
Sometimes people confuse satellite constellation with satellite cluster, satellite program, and satellite fleet.
A satellite cluster is a group of satellites doing orbital motion very close to each other in identical orbits. A satellite program is the generation of satellites that are launched in a successive manner. While satellite fleets are collections of satellites that operate independently i.e., not as a system but belong to the same manufacturer or operator.
Basics of Satellite Constellation
We have already discussed in our previous contents, that every space mission consists of three segments namely:
- Space segment
- Ground segment
- User Segment
So, here, the space segment is the satellite constellation, the ground segment includes the various ground stations responsible for controlling and monitoring of the events taking place in the space and the user segment that corresponds to the various I/O devices like smartphones, gateway, etc. i.e., the base stations. Sometimes the term ground terminal is used for the communication devices present at the ground level to combinedly denote the ground and user terminal.
LEO Satellite Constellation
The concept of the satellite constellation came several years ago and this was proved when Iridium and Globalstar came into existence. The use of these satellite constellations has greatly competed with the terrestrial cellular network. But got limited success as their cost of offering services was quite large. This can be understood in a way that during those days the proposed model of satellite constellation was less sustainable because the market was comparatively small and the initial and maintenance costs were quite high.
However, with the advent of technology, various advancements have been included and constellations have become a major asset relative to the field of communication.
When considered LEO constellation there are generally three categories in which data traffic is classified, namely, user data, control data, and telemetry and telecommand data. The control data is exchanged between ground stations and the satellites. The downlink sends the telemetry parameters like status, the configuration of payload, and subsystems. While the uplink receives the commands relative to controlling of mission operations.
The figure below represents a sketch of four logical links in LEO constellation: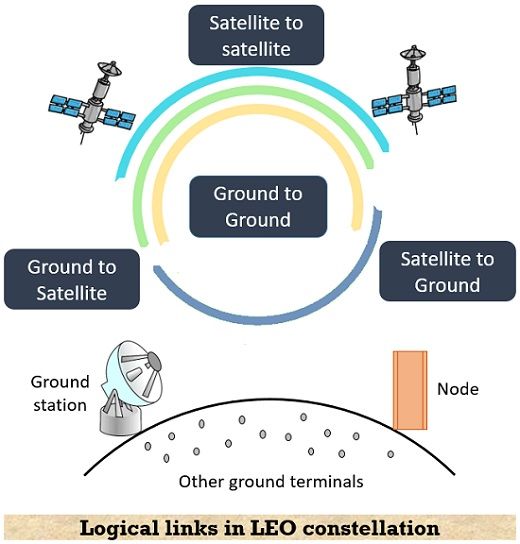
Let us now understand the four logical links illustrated above:
- G2G: This corresponds to a ground to a ground connection. Through this link, information is transported between two separate points on the ground where the sole purpose includes routing, handover, or coordinating.
- G2S: This is the ground to a satellite link. The control operations initiated by the ground stations are maintained via this link. This is inclusive of distributing instructions, routing along with caching, and telecontroling.
- S2G: This denotes satellite to ground link. This link comes into action when the signal from the ground station is received by the satellites in space and in response to that the satellite transmits application data like earth observation towards the ground-based station. This includes fault detection and telemetry.
- S2S: This corresponds to the satellite to satellite link. And it is of great significance when multiple satellites are operating as a system in the orbital plane. This link helps in controlling applications like sensing, routing, distributed processing along with topology management, and various autonomous operations.
It is to be noted here that the physical and logical links used to establish the network depend on the actual application.
How a satellite constellation system is described?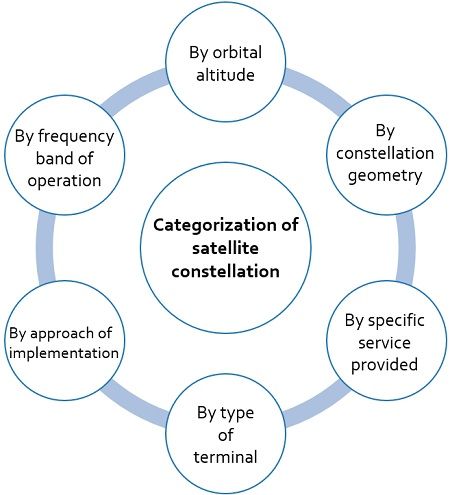
List of Satellite Constellation
The names of some well-known satellite constellations are as follows:
- Global Positioning System (GPS)
- Galileo
- GLONASS
- BeiDou
- NAVIC
- Iridium
- Globalstar
- Orbocomm
- Teledesic
- Starlink
- Eutelsat
- ViaSat
- O3b
- Iridium NEXT
Applications
From this discussion, we have got the idea that designing, building, and deploying satellites for various applications has become an important task over the past decades. The various applications of satellite constellation are as follows:
- In the field of communication
- Remote sensing and mining
- In maritime and aeronautics
- Satellite Navigation
- Mobile telephony
It is to be noted here that due to the motion of satellite and handover within the system, path delays exist in the network. But satellite constellation considers ground-based and space-based approach with or without the use of complex switching satellites.